Bloodborne Pathogens and the Typical American Worker
Bloodborne pathogens are infectious diseases living in bodily fluids. In 1992, OSHA (the Occupational Safety & Health Administration) recognized these potential hazards and issued a standard designed to "limit occupation exposure to blood and any other potentially infectious materials". How do bloodborne pathogens affect the typical American worker? Even though we might not be healthcare workers, or expect to come in contact with bodily fluids at work, all of us need to understand the risks and know how to protect ourselves. So, in this brief article, we are going to equip ourselves to do just that. Below, we highlight what a bloodborne pathogen is, how it is transmitted, and how we can protect ourselves from exposure.
What is a bloodborne pathogen?
A bloodborne pathogen is a microorganism that lives inside human blood, urine, feces, vomit, semen, vaginal secretions, saliva, and others. Examples of these pathogens are Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV, the virus that causes AIDS. Anyone exposed to these pathogens is at risk for serious or life-threatening illnesses.
"Any bodily fluid should be considered potentially infectious."
How are bloodborne pathogens transmitted?
Infectious pathogens are transmitted through bodily fluids. Any bodily fluid should be considered potentially infectious. The bodily fluids mentioned above are passed when they leave the infected person and enter the unsuspecting victim. This can happen through a blood-to-blood interaction between the infected person and the worker or in some cases fluid-to-fluid transmission. It can take place through a sexual act, needle stick, splash or spray, or even something like hand-to-eye or hand-to-mouth where your hand is exposed and then you rub your face. Some bloodborne pathogens can live outside the body for over a week. While this may sound alarming, using the correct precautions will help limit exposure.
How can I protect myself?
Understanding what a bloodborne pathogen is and the risks involved is the first and most important step in protecting ourselves. Below are 7 ways we can reduce our exposure and limit our risks.
1. Learn & Equip yourself - Take time to read about bloodborne pathogens from reliable sources like the CDC or OSHA. Educate yourself and learn about the risks and what to do about it. (Be trained if necessary).
2. Universal Precautions - Consider any bodily fluid potentially infectious. In the healthcare industry, they call this Universal Precautions. Always assume and respond as if it is potentially infectious.
3. Engineer out your exposure - Limit your risk to exposure before it happens. An example would be to use an approved sharps container to collect used needles or other sharps that could cause a "stick" in an unsuspecting worker.
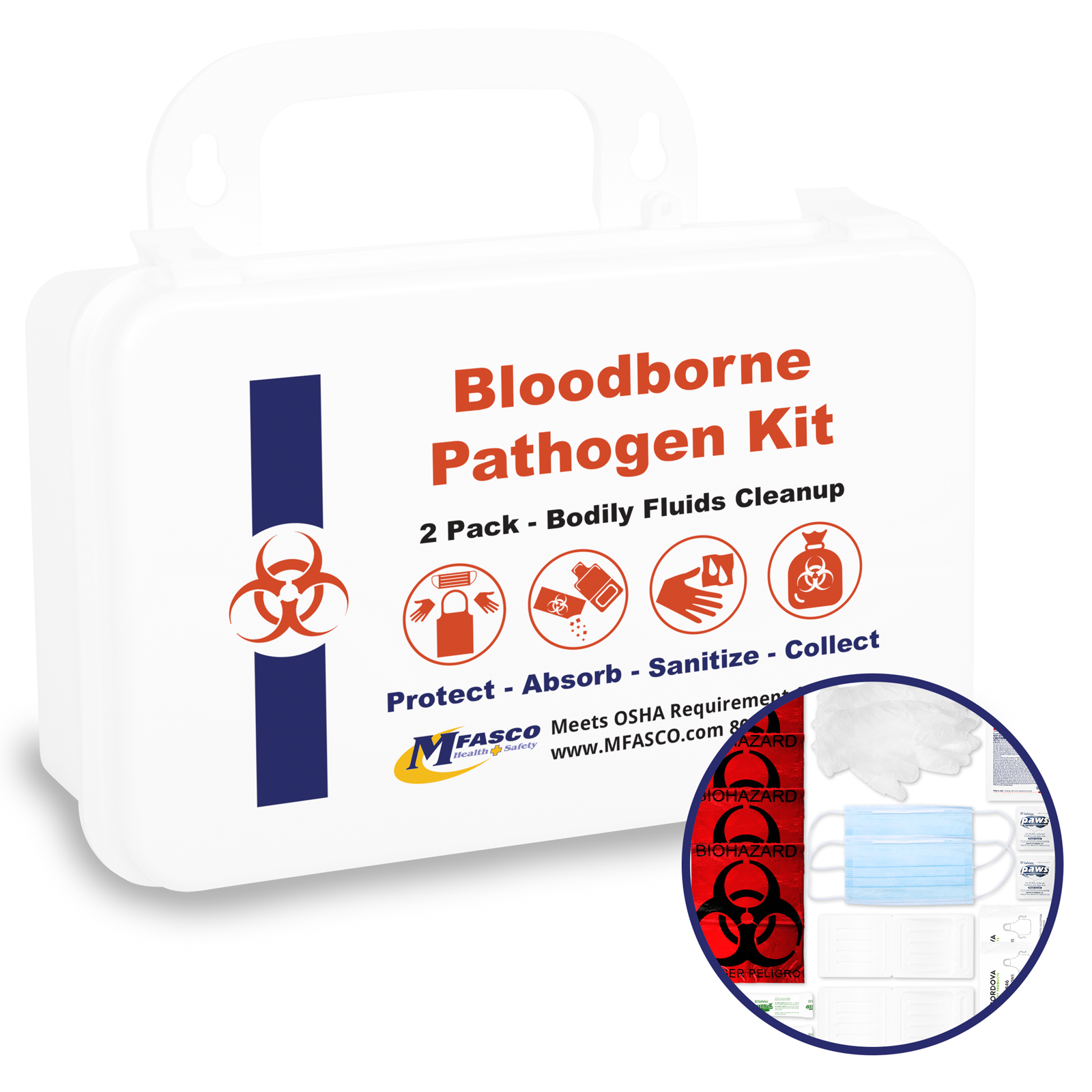
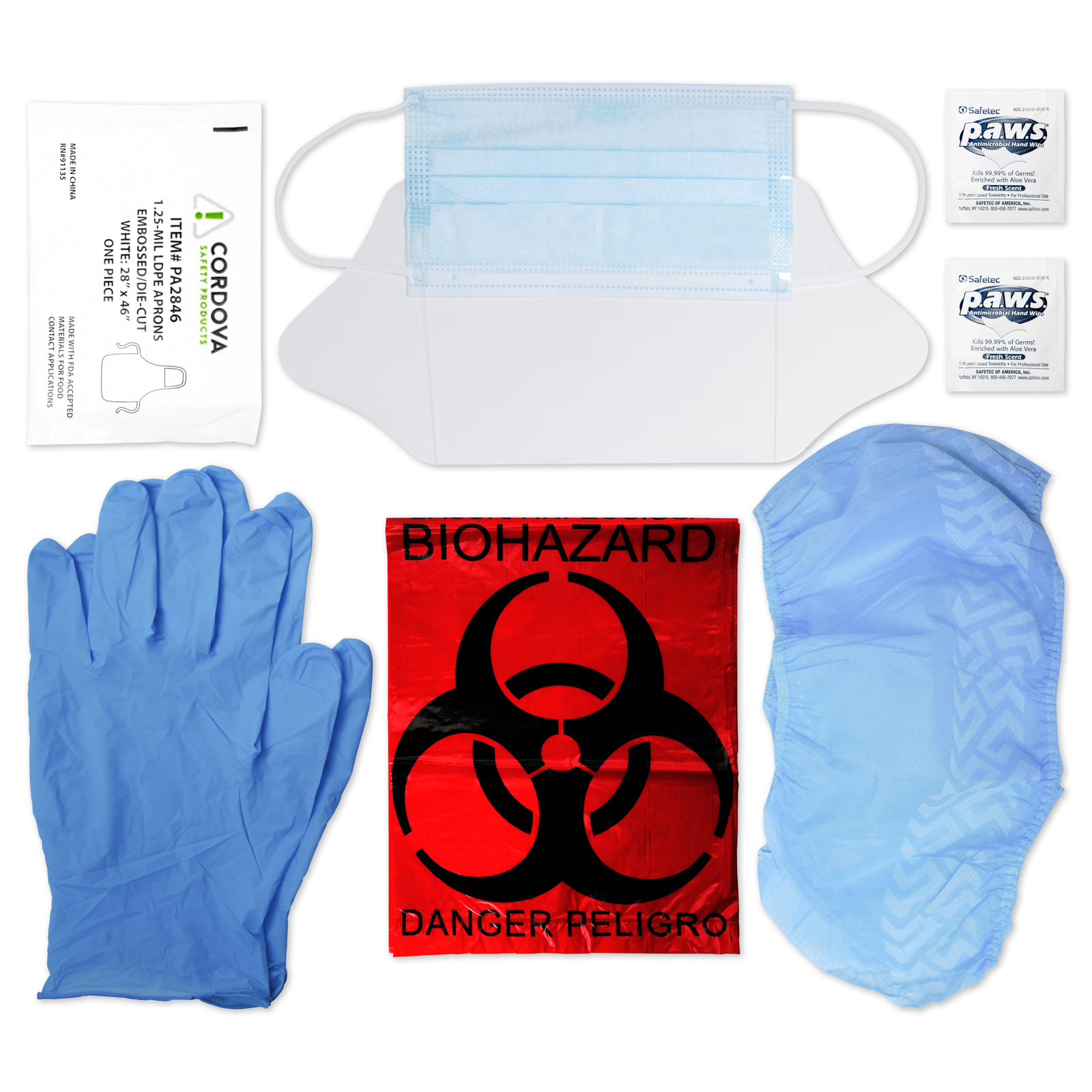
4. Wear the appropriate PPE - Whenever you can reasonably anticipate exposure to bloodborne pathogens, always wear the necessary PPE. Examples would be gloves, gowns, masks, mouthpieces, and resuscitation bags.
5. Dispose of the potentially infectious PPE or other clothing properly - If clothes or PPE have been exposed to bodily fluids, be sure to remove them and dispose of them properly.
6. Proper decontamination of the exposed area and surfaces - Bio Safety clean-up kits usually include bleach or other approved disinfectants that clean surfaces where exposure took place. The OSHA standard goes into detail about the proper process.
7. Wash hands - As always, proper hand washing immediately after exposure is critical.
We live in an age where bloodborne pathogens are around us. Understanding what they are, how they are transmitted, and how we can protect ourselves reduces the risk of exposure. See these links to learn more about Bloodborne Pathogens and the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The average American worker who is not part of the Health Care industry is not required by law to follow the standard BUT all of us should be informed and aware of the risks and understand how we should respond.
Bio Safety Products & Accessories
MFASCO's Make a Kit Tool
Bio Protection Products
Deluxe PPE & Clean Up Kit Plastic
Additional Resources for Bio Safety Kits & Supplies
Top 8 First Aid Kit Types
Disinfecting hard Surfaces for Workplace Health
Understanding the Importance of PPE for Bodily Fluids
Contributing Expert

Mike Brinker
Mike Brinker has been working in the first aid industry for over 35 years. He has worked with thousands of businesses,groups, and organizations to provide a healthy and safe work environment. Mike helped create “Make-A-Kit”, the internet's only online first aid kit creation tool. He has also authored many helpful first-aid and safety-related resource articles found at the MFASCO Learning Center.